Objective 🎯
Transform a request in a stand-alone object allowing to pass it as a method argument, delay or queue its execution also providing an interface to undo what was done.
Type ✅
✔️Behavioral: Describes how objects interact/communicate between themselves.
❌Creational: Describes how to instantiate an object without large and complex.
❌Structural: Describes how objects/classes are composed to form larger structures.
UML 📐
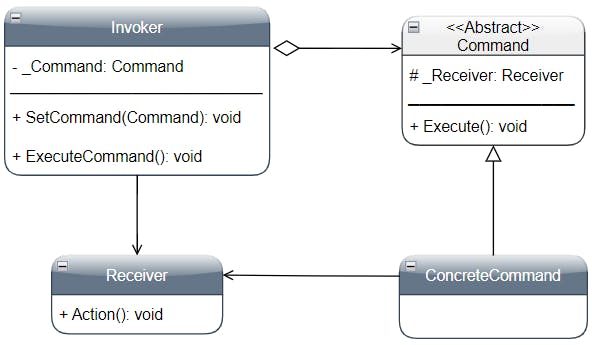
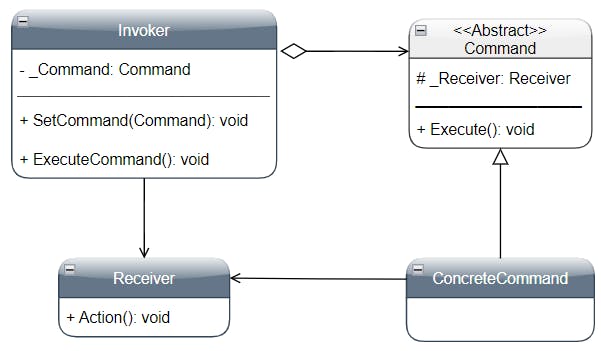
Participants 🔗
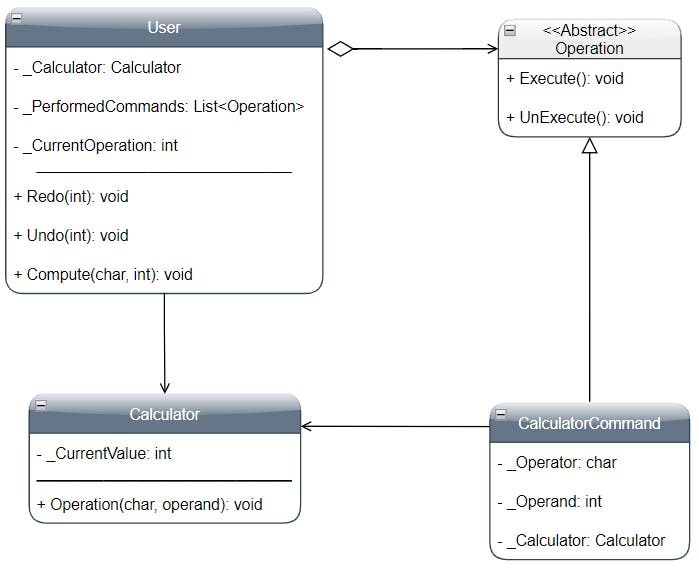
• Command:
- Declares an interface for executing an operation
• ConcreteCommand:
- Represents the binding between a Receiver object and an action
- Implements the method Execute by invoking the corresponding operation(s) on Receiver
• Invoker:
- Asks to the Command object to execute the request
• Receiver:
- Knows how to perform the operations associated with the request
Sample Code 🎮
Structural Example 🏛️
public static class CommandStructural
{
public static void Execute()
{
Receiver lReceiver = new Receiver();
Command lCommand = new ConcreteCommand(lReceiver);
Invoker lInvoker = new Invoker();
lInvoker.SetCommand(lCommand);
lInvoker.ExecuteCommand();
}
}
public abstract class Command
{
protected Receiver _Receiver;
public Command(Receiver prReceiver)
{
_Receiver = prReceiver;
}
public abstract void Execute();
}
public class ConcreteCommand : Command
{
public ConcreteCommand(Receiver prReceiver) :
base(prReceiver)
{
}
public override void Execute()
{
_Receiver.Action();
}
}
public class Receiver
{
public void Action()
{
Console.WriteLine("Called Receiver.Action()");
}
}
public class Invoker
{
private Command _Command;
public void SetCommand(Command prCommand)
{
_Command = prCommand;
}
public void ExecuteCommand()
{
_Command.Execute();
}
}
Output
Real-world Example 🔥
public static class CommandPractical
{
public static void Execute()
{
User lUser = new User();
// User presses calculator buttons
lUser.Compute('+', 100);
lUser.Compute('-', 50);
lUser.Compute('*', 10);
lUser.Compute('/', 2);
// Undo 4 commands
lUser.Undo(4);
// Redo 3 commands
lUser.Redo(3);
}
}
public abstract class Operation
{
public abstract void Execute();
public abstract void UnExecute();
}
class CalculatorCommand : Operation
{
private char _Operator;
private int _Operand;
private Calculator _Calculator;
public CalculatorCommand(Calculator prCalculator,
char prOperator, int prOperand)
{
_Calculator = prCalculator;
_Operator = prOperator;
_Operand = prOperand;
}
public char Operator
{
set { _Operator = value; }
}
public int Operand
{
set { _Operand = value; }
}
public override void Execute()
{
_Calculator.Operation(_Operator, _Operand);
}
public override void UnExecute()
{
_Calculator.Operation(Undo(_Operator), _Operand);
}
private char Undo(char prOperator)
{
switch (prOperator)
{
case '+': return '-';
case '-': return '+';
case '*': return '/';
case '/': return '*';
default: throw new ArgumentException(prOperator.ToString());
}
}
}
public class Calculator
{
private int _CurrentValue = 0;
public void Operation(char prOperator, int prOperand)
{
int lValueBefore = _CurrentValue;
switch (prOperator)
{
case '+': _CurrentValue += prOperand; break;
case '-': _CurrentValue -= prOperand; break;
case '*': _CurrentValue *= prOperand; break;
case '/': _CurrentValue /= prOperand; break;
}
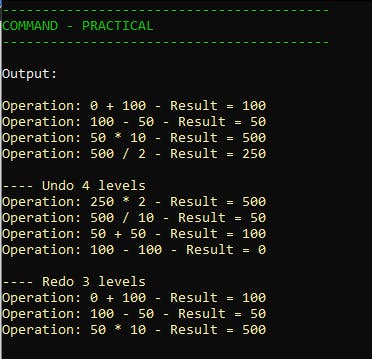
Console.WriteLine($"Operation: {lValueBefore} {prOperator} {prOperand} - Result = {_CurrentValue}");
}
}
public class User
{
private Calculator _Calculator = new Calculator();
private List<Operation> _PerformedCommands = new List<Operation>();
private int _CurrentOperation = 0;
public void Redo(int prLevels)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n---- Redo {0} levels ", prLevels);
for (int i = 0; i < prLevels; i++)
{
if (_CurrentOperation < _PerformedCommands.Count - 1)
{
Operation lOperation = _PerformedCommands[_CurrentOperation];
lOperation.Execute();
_CurrentOperation++;
}
}
}
public void Undo(int prLevels)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n---- Undo {0} levels ", prLevels);
for (int i = 0; i < prLevels; i++)
{
if (_CurrentOperation > 0)
{
_CurrentOperation--;
Operation lOperation = _PerformedCommands[_CurrentOperation] as Operation;
lOperation.UnExecute();
}
}
}
public void Compute(char prOperator, int prOperand)
{
Operation lCommand = new CalculatorCommand(_Calculator, prOperator, prOperand);
lCommand.Execute();
_PerformedCommands.Add(lCommand);
_CurrentOperation++;
}
}
Output